Fatigue Analysis
Long term Damage Prevention
CANEIL personnel have performed a wide range of Fatigue Analysis projects. Protection against failure from cyclic loading, in other words a Fatigue Analysis, is required when a pressure vessel is operating in cyclic service. CANEIL uses SOLIDWORKS Premium software to create comprehensive studies using the applicable loading conditions to analyze vessel components for fatigue.
General Steps we Follow
Gather all necessary information, including but not limited to:
- Vessel Drawing and Manufacturers Data Report to build the model
- Inspection Reports to know if there are any defects present in the vessel that need to be included in the model.
- Historical operating pressure and temperature data which is used to build the loading history.
Perform Fatigue Screening Analysis using ASME Sec VIII Div.2 Part 5.
- Determine loading history including all pressure and temperature cycles.
- Based off the loading history and if the vessel is of integral or non-integral construction, it will determine if a full fatigue analysis is required.

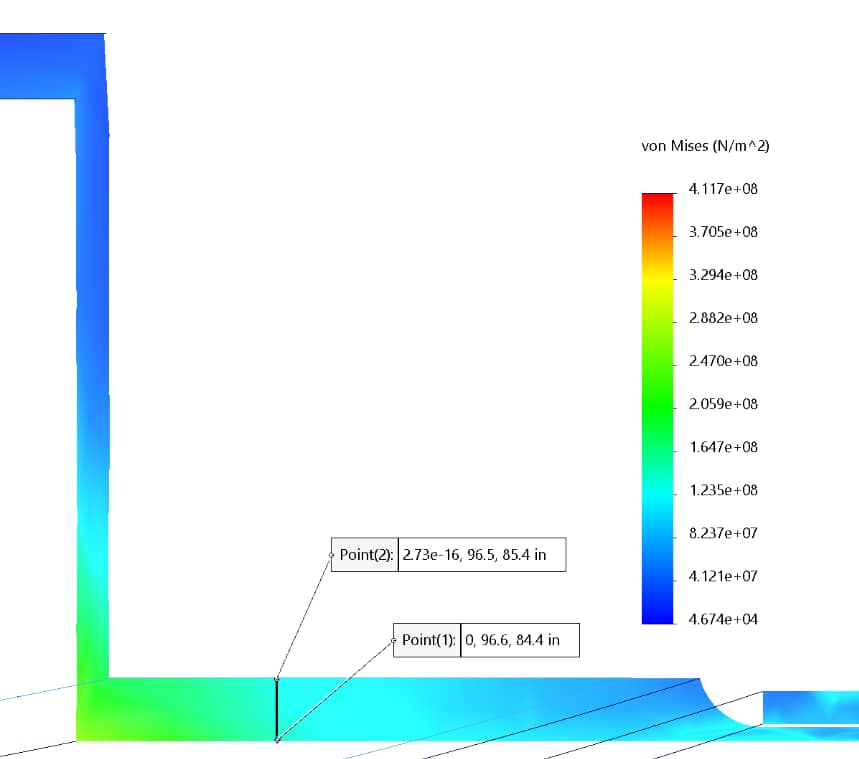
If it was determined through the analysis of the fatigue screening criterion a full fatigue analysis is required, then a model of the vessel is created and an FEA analysis is performed to evaluate the stress at critical vessel locations
To extract the stress values from the SOLIDWORKS model to be used in the fatigue analysis, the stress is linearized at areas of interest to gather the stress values required as per ASME Sec VIII Div. 2 Part 5. The fatigue analysis criterion are then evaluated to determine if the vessel components being analyzed are safe for continued operation.
The following is a summary of just a few of the projects our team has undertaken:
A 4 ft diameter Butane Treater in sweet service was operating in cyclic service. Due to the nature of the service it was determined that a fatigue assessment using the criteria from ASME Sec VIII Div.2 part 5.5 was required. A loading history for the treater was established from operating history to determine if a full fatigue analysis was required. The butane treater was modelled in SolidWorks and a simulation was run to determine the stress concentrations in areas of concern for the vessel. The following analyses were conducted and corresponding criteria were checked as part of the Fatigue Assessment:
- Loading history which includes all cyclic operating loads was determined using the Rainflow Counting Method from Annex 5-B.4 of ASME Sec VIII Div.2 and Section 5.4.4 from ASTM E1049.
- Fatigue analysis screening using Method A from Section 5.5.2.3 of ASME Sec VIII Div.2.
- Protection against failure due to cyclic loading was verified by checking the accumulated fatigue damage in the model against the criterion from ASME Sec. VIII Div. 2 Part 5.5.4.2.
A 3 ft diameter Mol Sieve in sweet service was operating in cyclic service. Due to the nature of the service it was determined that a fatigue assessment using the criteria from ASME Sec VIII Div.2 part 5.5 was required. A loading history for the treater was established from operating sequence data, as no historical cyclic operating load data was available, to determine if a full fatigue analysis was required. The mol sieve was modelled in SolidWorks and a simulation was run to determine the stress concentrations in areas of concern for the vessel. The following analyses were conducted and corresponding criteria were checked as part of the Fatigue Assessment:
- Fatigue analysis screening using Method A from Section 5.5.2.3 of ASME Sec VIII Div.2.
- Protection against failure due to cyclic loading was verified by checking the accumulated fatigue damage in the model against the criterion from ASME Sec. VIII Div. 2 Part 5.5.4.2.
A 12 ft diameter condensate storage bullet was operating in cyclic service. Due to the nature of the service it was determined that a fatigue assessment using the criteria from ASME Sec VIII Div.2 part 5.5 was required. A loading history for the treater was established from operating history to determine if a full fatigue analysis was required. The number of operating cycles over the operating life of the vessel was determined to be less than the fatigue screen criteria in Table 5.9 of ASME Sec VIII Div. 2 part 5, and therefore a full fatigue analysis was not carried out. The following analyses were conducted and corresponding criteria were checked as part of the fatigue screening assessment:
- Fatigue analysis screening using Method A from Section 5.5.2.3 of ASME Sec VIII Div.2.

